Configuring QLogic BIOS to Boot from SAN
1. Take it into legacy mode
Go to Compute > BIOS
2. Configure Boot order
Boot order also must be created . Go to Compute > BIOS > Configuration Order
Name : SAN-BOOT-ORDER
Status : Enabled
Order : 1
Slot : 4
LUN : 0 ( Note : LUN ID must be verified from storage )
Name : SAN-BOOT-ORDER
Status : Enabled
Order : 1
Slot : 6
LUN : 0 ( Note : LUN ID must be verified from storage )
3. While booting the server, press Ctrl-Q to enter the Fast!UTIL configuration utility.
4. Do one of the following :
- If you have only one host bus adapter (HBA), it is selected automatically, and the Fast!UTIL Options screen appears.
- If you have more than one HBA, you need to select it manually. In the Select Host Adapter screen, use the cursor keys to select the chosen HBA and press Enter.Note: Booting from SAN requires choosing the lowest numbered HBA that has any LUNs visible.
As you can see we have 2 HBA card and total in 4 ports . Now we need to select all those 4 ports inorder to use all of the 4 ports for booting from the lun in case of failover.
In the Fast!UTIL Options screen, select Configuration Settings and press Enter. ( Noted : Inorder to use all 4 ports we need to configure it all of the 4 ports available.)
Go to Adapter Settings and enable Host Adapter BIOS
Then go into Selectable boot settings and enabled selectable boot
NOTE : You will need to enable selectable boot and Host adapter BIOS in all 4 ports available which has not been displayed in this blog.
5. You will ne able to see the initiator in your storage as well.
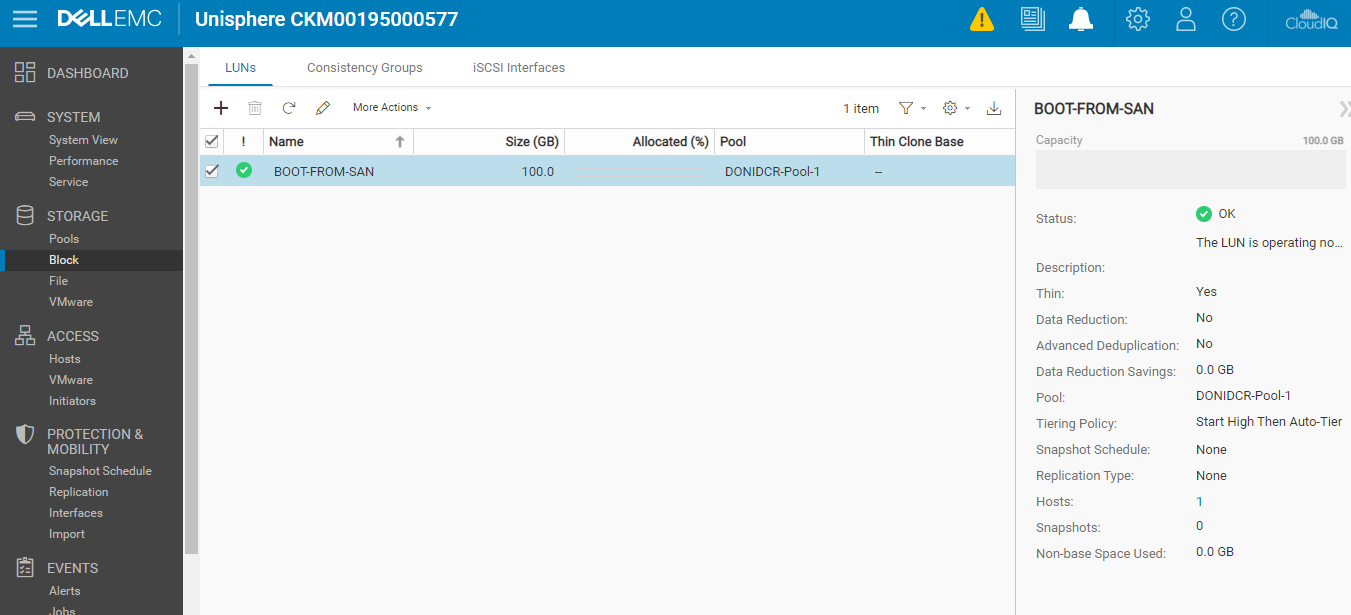
You will now need to create a LUN and attached the host accordingly.
As you can see in the below screenshot LUN has been detected.
https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/1448














Comments
Post a Comment